

See also: Strength of Materials Ultimate Tensile Strength of Fluorine Yield strength or yield stress is the material property defined as the stress at which a material begins to deform plastically whereas yield point is the point where nonlinear (elastic + plastic) deformation begins. Strength of a material is its ability to withstand this applied load without failure or plastic deformation.įor tensile stress, the capacity of a material or structure to withstand loads tending to elongate is known as ultimate tensile strength (UTS). In designing structures and machines, it is important to consider these factors, in order that the material selected will have adequate strength to resist applied loads or forces and retain its original shape. Strength of materials basically considers the relationship between the external loads applied to a material and the resulting deformation or change in material dimensions. Is the element sodium stable or unstable? So if fluorine were the most electronegative in terms of acidity, it would be the opposite in terms of base classification.In mechanics of materials, the strength of a material is its ability to withstand an applied load without failure or plastic deformation. Fluorine | F2 | CID 24524 - structure, chemical names, physical and chemical properties, classification, patents, literature, biological activities, safety/hazards/toxicity information, supplier lists, and more. Francium is a largest and heaviest alkali metal with also means it … All the elements of similar categories show a lot of similarities and differences in their chemical, atomic, physical properties and uses. Its copolymerization with tetrafluoroethylene yields nitroso rubber, one of the most chemically stable fluorine rubbers. Difluoromethanol and trifluoromethanol have not. With a standard atomic weight of circa 1.008, hydrogen is the lightest element on the periodic table. Hydrogen is a chemical element with atomic number 1 which means there are 1 protons and 1 electrons in the atomic structure.The chemical symbol for Hydrogen is H. A stable electron configuration refers to an atom in which the outermost (valence) shell is complete. Therefore, since fluorine has a higher electronegatvity than chlorine, fluorine is more reactive. Soil, water, plants, and foods contain trace amounts of fluoride.
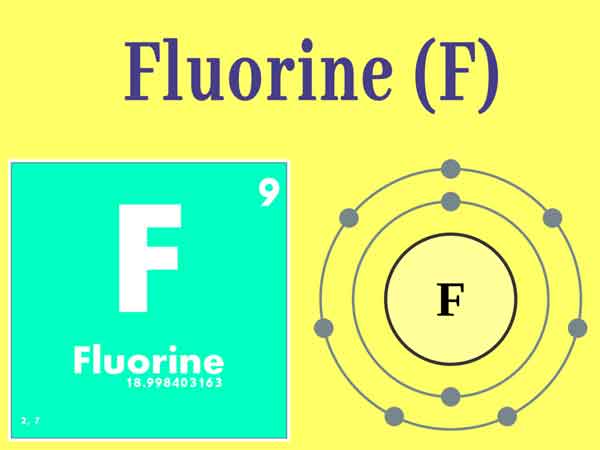
An example of a radionuclide produced in an accelerator is fluorine-18. Strong acids and bases are less stable than weak acids and bases because they are more reactive. Why? Monofluoromethanol is an unstable liquid with a boiling point of 51☌. Fluorine is the only element which will shape compounds with noble gasses xenon, krypton, and radon. The elements with which it doesn't respond are oxygen, helium, neon, and argon. Fluorine is the most receptive and most electronegative of all the chemical elements. Groundwater and soil in most parts of the world contain small amounts of fluoride, and these ions can replace the hydroxyl ions in bone mineral to form fluorapatite. Two more electrons or a double bond will make it unstable. Hydrogen is a chemical element with atomic number 1 which means there are 1 protons and 1 electrons in the atomic structure. Only fluorine-19 is stable and naturally occurring in more than trace quantities therefore, fluorine is a monoisotopic and mononuclidic element. The thermal stability increases with increasing cationic size. Like all alkali metals, lithium is highly reactive and flammable, and is stored in mineral … Cu+ gets oxidized in an aqueous solution to get a stable configuration of Cu2+. Without going into too much detail, an element's radioactivity corresponds to the ratio between protons and neutrons it has in its nucleus. Fluorine is a generally unpleasant substance. For this reason, it can accommodate only atoms that are smaller in size, i.e., fluorine being smaller in size it can form a better bond with nitrogen. Creating this type of hypercoordinate compounds requires two sets of four-electron three-centre bonds of the $\ce$’s lesser stability is the lower electronegativity of chlorine. Hence, the oxidation state of oxygen must be higher than that of fluorine in positive sense. This excess energy can be used in one of three ways: emitted from the nucleus as gamma radiation transferred to one of its electrons to release it as a conversion electron or used to create and emit a new particle (alpha particle or beta particle) … Fluorine is the most reactive of the chemical elements, it is also generally linked to other elementsa. Which orbital is the most stable? A single atom of helium is stable in nearly all circumstances.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
